You can access international investment opportunities by investing with emerging markets bond fund funds. However, these funds carry risks that are distinct from other types of investments. These risks can include currency fluctuations, political instability, economic risks, interest rate risk, and issuer default risk. They can also increase your risk of capital losses.
Emerging market bond funds usually invest in foreign-denominated bonds issued by sovereign countries. They can face higher volatility and lower liquidity because these funds are not subject to the strict regulations of international securities markets. These funds also present a number of unique risks, including credit risk, currency exchange rate risk, and issuer default risk.
The JPMorgan EMBI Global Diversified Index is a market-capitalization-weighted index that tracks debt instruments issued by sovereign entities. The index also includes Eurobonds as well as local-currency sovereign loans.
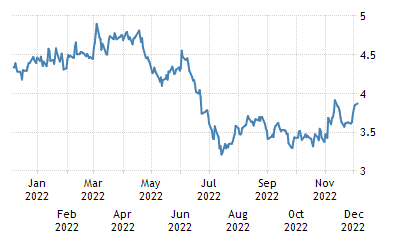
The Bloomberg Barclays Emerging Markets USD Agregate bond index lost 1.3 percent in the last six weeks. This has occurred on the back of a continued weakness in the eurozone, as well as the spread of the Ebola virus in west Africa. Investors have been forced to withdraw from emerging market bonds and other risk assets as a result. However, a number of commentators have argued that the recent correction has left emerging market debt more attractive than it was before.
One fund that has been successful in incorporating emerging markets into its portfolio is the Harding Loevner Institutional Emerging Markets Fund. Although it comes with a higher level of risk than its Morningstar peers, it still offers higher returns. Additionally, managers of this fund typically hold at least 50% of their assets in corporate bond.
Another fund to consider: the iShares JPMorgan USD Emerging Markets Bond. This fund tracks a basket of US dollar-denominated emerging markets debt instruments, with the exception of Venezuelan sovereign debt. It also holds defaulted bonds. However, its allocation to Venezuelan debt is relatively low. The fund is able to hold a number of other issues, such as restructured debt. Investors can choose from a variety of investment options, at low cost.
Emerging markets bond fund are a good way for diversifying your portfolio in the long-term. However, investors must consider the inherent risk of investing in bonds. These risks can also have an adverse effect on the industry or the particular sector that the fund works in. This is especially true when bonds are issued by foreign governments.

Emerging markets bond funds work best as a supporting investment rather than a core asset in a balanced portfolio. However, if you have an interest in this sector, you may consider a variety of emerging markets bond ETFs, which provide a wide range of nuanced bonds and robust liquidity. These ETFs are often cheaper than other emerging markets bond mutual funds and can be a cost-saving alternative to individual bonds.
FAQ
Why are marketable securities important?
An investment company exists to generate income for investors. This is done by investing in different types of financial instruments, such as bonds and stocks. These securities offer investors attractive characteristics. These securities may be considered safe as they are backed fully by the faith and credit of their issuer. They pay dividends, interest or both and offer growth potential and/or tax advantages.
Marketability is the most important characteristic of any security. This is the ease at which the security can traded on the stock trade. You cannot buy and sell securities that aren't marketable freely. Instead, you must have them purchased through a broker who charges a commission.
Marketable securities are government and corporate bonds, preferred stock, common stocks and convertible debentures.
These securities are preferred by investment companies as they offer higher returns than more risky securities such as equities (shares).
What is security in a stock?
Security is an investment instrument whose value depends on another company. It could be issued by a corporation, government, or other entity (e.g. prefer stocks). The issuer promises to pay dividends and repay debt obligations to creditors. Investors may also be entitled to capital return if the value of the underlying asset falls.
How do you choose the right investment company for me?
You want one that has competitive fees, good management, and a broad portfolio. Commonly, fees are charged depending on the security that you hold in your account. Some companies don't charge fees to hold cash, while others charge a flat annual fee regardless of the amount that you deposit. Others may charge a percentage or your entire assets.
It's also worth checking out their performance record. A company with a poor track record may not be suitable for your needs. Avoid companies with low net assets value (NAV), or very volatile NAVs.
Finally, it is important to review their investment philosophy. To achieve higher returns, an investment firm should be willing and able to take risks. If they are unwilling to do so, then they may not be able to meet your expectations.
What is a bond and how do you define it?
A bond agreement between two people where money is transferred to purchase goods or services. It is also known by the term contract.
A bond is usually written on paper and signed by both parties. The document contains details such as the date, amount owed, interest rate, etc.
When there are risks involved, like a company going bankrupt or a person breaking a promise, the bond is used.
Many bonds are used in conjunction with mortgages and other types of loans. This means that the borrower has to pay the loan back plus any interest.
Bonds are also used to raise money for big projects like building roads, bridges, and hospitals.
It becomes due once a bond matures. This means that the bond owner gets the principal amount plus any interest.
Lenders can lose their money if they fail to pay back a bond.
What is the difference in marketable and non-marketable securities
Non-marketable securities are less liquid, have lower trading volumes and incur higher transaction costs. Marketable securities, however, can be traded on an exchange and offer greater liquidity and trading volume. Marketable securities also have better price discovery because they can trade at any time. But, this is not the only exception. Some mutual funds, for example, are restricted to institutional investors only and cannot trade on the public markets.
Non-marketable security tend to be more risky then marketable. They have lower yields and need higher initial capital deposits. Marketable securities are usually safer and more manageable than non-marketable securities.
For example, a bond issued in large numbers is more likely to be repaid than a bond issued in small quantities. The reason for this is that the former might have a strong balance, while those issued by smaller businesses may not.
Because of the potential for higher portfolio returns, investors prefer to own marketable securities.
Stock marketable security or not?
Stock is an investment vehicle that allows you to buy company shares to make money. This can be done through a brokerage firm that helps you buy stocks and bonds.
You could also choose to invest in individual stocks or mutual funds. There are actually more than 50,000 mutual funds available.
There is one major difference between the two: how you make money. With direct investment, you earn income from dividends paid by the company, while with stock trading, you actually trade stocks or bonds in order to profit.
In both cases, you are purchasing ownership in a business or corporation. If you buy a part of a business, you become a shareholder. You receive dividends depending on the company's earnings.
Stock trading is a way to make money. You can either short-sell (borrow) stock shares and hope the price drops below what you paid, or you could hold the shares and hope the value rises.
There are three types stock trades: put, call and exchange-traded funds. Call and put options give you the right to buy or sell a particular stock at a set price within a specified time period. ETFs are similar to mutual funds, except that they track a group of stocks and not individual securities.
Stock trading is very popular as it allows investors to take part in the company's growth without being involved with day-to-day operations.
Stock trading is a complex business that requires planning and a lot of research. However, the rewards can be great if you do it right. This career path requires you to understand the basics of finance, accounting and economics.
What is the difference?
Brokers are specialists in the sale and purchase of stocks and other securities for individuals and companies. They handle all paperwork.
Financial advisors are experts in the field of personal finances. Financial advisors use their knowledge to help clients plan and prepare for financial emergencies and reach their financial goals.
Financial advisors can be employed by banks, financial companies, and other institutions. They may also work as independent professionals for a fee.
You should take classes in marketing, finance, and accounting if you are interested in a career in financial services. Also, it is important to understand about the different types available in investment.
Statistics
- For instance, an individual or entity that owns 100,000 shares of a company with one million outstanding shares would have a 10% ownership stake. (investopedia.com)
- The S&P 500 has grown about 10.5% per year since its establishment in the 1920s. (investopedia.com)
- Even if you find talent for trading stocks, allocating more than 10% of your portfolio to an individual stock can expose your savings to too much volatility. (nerdwallet.com)
- Individuals with very limited financial experience are either terrified by horror stories of average investors losing 50% of their portfolio value or are beguiled by "hot tips" that bear the promise of huge rewards but seldom pay off. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to open an account for trading
To open a brokerage bank account, the first step is to register. There are many brokers available, each offering different services. There are many brokers that charge fees and others that don't. Etrade, TD Ameritrade Fidelity Schwab Scottrade Interactive Brokers are some of the most popular brokerages.
Once you've opened your account, you need to decide which type of account you want to open. One of these options should be chosen:
-
Individual Retirement Accounts, IRAs
-
Roth Individual Retirement Accounts
-
401(k)s
-
403(b)s
-
SIMPLE IRAs
-
SEP IRAs
-
SIMPLE 401(k).
Each option has its own benefits. IRA accounts have tax advantages but require more paperwork than other options. Roth IRAs are a way for investors to deduct their contributions from their taxable income. However they cannot be used as a source or funds for withdrawals. SIMPLE IRAs have SEP IRAs. However, they can also be funded by employer matching dollars. SIMPLE IRAs are very simple and easy to set up. These IRAs allow employees to make pre-tax contributions and employers can match them.
Finally, you need to determine how much money you want to invest. This is also known as your first deposit. A majority of brokers will offer you a range depending on the return you desire. You might receive $5,000-$10,000 depending upon your return rate. This range includes a conservative approach and a risky one.
After choosing the type of account that you would like, decide how much money. Each broker has minimum amounts that you must invest. The minimum amounts you must invest vary among brokers. Make sure to check with each broker.
After you've decided the type and amount of money that you want to put into an account, you will need to find a broker. Before you choose a broker, consider the following:
-
Fees-Ensure that fees are transparent and reasonable. Brokers will often offer rebates or free trades to cover up fees. However, some brokers charge more for your first trade. Be wary of any broker who tries to trick you into paying extra fees.
-
Customer service - Find customer service representatives who have a good knowledge of their products and are able to quickly answer any questions.
-
Security - Choose a broker that provides security features such as multi-signature technology and two-factor authentication.
-
Mobile apps – Check to see if the broker provides mobile apps that enable you to access your portfolio wherever you are using your smartphone.
-
Social media presence. Find out whether the broker has a strong social media presence. If they don’t, it may be time to move.
-
Technology - Does this broker use the most cutting-edge technology available? Is the trading platform simple to use? Is there any difficulty using the trading platform?
Once you have selected a broker to work with, you need an account. While some brokers offer free trial, others will charge a small fee. After signing up you will need confirmation of your email address. Next, you'll need to confirm your email address, phone number, and password. Finally, you will need to prove that you are who you say they are.
After you have been verified, you will start receiving emails from your brokerage firm. These emails will contain important information about the account. It is crucial that you read them carefully. You'll find information about which assets you can purchase and sell, as well as the types of transactions and fees. You should also keep track of any special promotions sent out by your broker. These may include contests or referral bonuses.
The next step is to open an online account. An online account can be opened through TradeStation or Interactive Brokers. Both of these websites are great for beginners. When opening an account, you'll typically need to provide your full name, address, phone number, email address, and other identifying information. After you submit this information, you will receive an activation code. This code will allow you to log in to your account and complete the process.
You can now start investing once you have opened an account!